Master Secretarial Audit: A Complete Compliance Guide
- April 27, 2024
- Start and manage a business

A secretarial audit involves detailed examination of a firm’s books and papers by an independent auditor or a firm that specializes in such audits. The primary objective of the Secretarial Audit under the Companies Act 2013 is to ensure compliance with various laws, rules, regulations and standards applicable to the company’s activities. These could be company laws, securities legislation, labor legislations, environment legislations, tax legislations and other regulatory requirements. Typically, an audit looks at how well a company has adhered to its legal and regulatory obligations including corporate governance; management practices; disclosure norms; procedural requirements. To ascertain compliance with these obligations different documents are examined such as meeting minutes, resolutions, statutory registers, regulatory filings, contracts/ agreements and other relevant records.
| Table of Content |
Applicability of Secretarial Audit – Section 204(1)
The applicability of secretarial Audit can be understood by understanding the Rule 9 of the Companies (Appointment and Remuneration of Managerial Personnel) Rules, 2014:
That applies to all
- listed companies;
- public companies having paid up share capital of Rs.50 crore or more;
- Public companies having turnover of Rs.250 crore or more.
- Every company which has loans or borrowings from banks or public financial institutions in excess of one hundred crore rupees.
Scope of Secretarial Audit
For the purposes of this form, Secretarial Auditor should assess and express opinion in relation to compliance with the following five specific Acts:
Companies Act 2013 and its provisions;
Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act 1956 (“SCRA”) and its rules.
Depositories Act of 1996 along with related regulations; Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 and its regulation for foreign direct investment, overseas direct investments & external commercial borrowing; Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (“SEBI Act”) regulations/guidelines.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (Buy Back of Securities) Regulations, 1998 Other areas which need to be checked Secretarial standards issued by the Institute of Company Secretaries of India; The SEBI (Listing and Other Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015, if applicable.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeovers) Regulations, 2011.
iii. Securities and Exchange Board of India (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations (1992).
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations of 2009.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (Employee Option and Share Purchase Scheme) Guidelines, 1999
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India’s (Issues and Listing of Debt Securities)
vii The Securities and Exchange Board of India (Registrars to Issue and Share Transfer Agents) Regulations, 1993.
Viii The Securities and Exchange Board of India’s Delisting of Equity Shares Regulations, 2009.
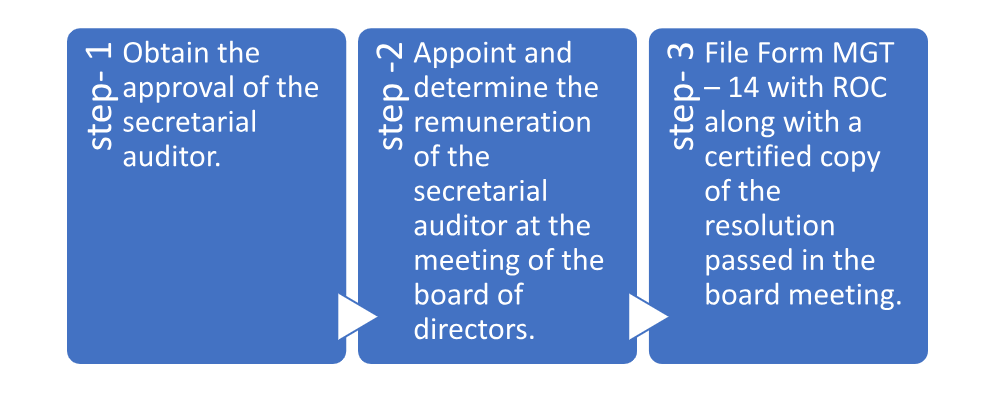
Appointment of Secretarial Auditor
According to Article 8(4) of the Company (Board of Directors’ Meeting and its Authority) Rules of 2014, the Secretary is appointed by a resolution passed at a properly convened meeting of the Company’s Board of Directors.
- Obtain approval from the auditor’s secretariat.
- Appoint and remunerate the secretary auditor at the board of directors’ meeting.\
iii. Submit Form MGT-14 to the ROC, together with a certified copy of the board meeting resolution.
- Secretarial Audit Report
Every company to which secretarial report applies –
It shall be prepared by a Company Secretary in Practice.
It shall be prepared in Form MR-3
Annexed with Board’s Report, considering the increasing importance of Corporate Governance.
Advantages of the Audit Secretarial
A Master Secretarial Audit offers several benefits, including ensuring compliance with legal and procedural standards and reducing the risk of legal concerns affecting the company’s progress.
Ensuring confidence among promoters, directors, investors, government agencies, regulators, and other stakeholders.
Ensure the company’s aims, structures, and operations align with current business trends and applicable legislation.
Improve the company’s reputation among regulators and stakeholders.
Use as a risk management tool for governance and compliance, mitigating regulatory hazards.
Assisting investors in assessing company compliance and making educated investment decisions.
Penal provisions relating to the Audit Secretariat
According to Section 204(4) of Secretarial Audit under the Companies Act 2013 the Companies Act 2013, if the company or any officer of the company or company secretary in practice violates the provisions of this section, the company, any officer of the company, or the company secretary in practice who is in default shall be fined two million rupees.
Conclusion
A secretarial audit under the Companies Act 2013 is a critical component of corporate governance and compliance, providing a clear lens through which to evaluate organizations’ compliance with legal and regulatory standards. Its contribution to improving openness, accountability, and governance processes cannot be emphasized. As the corporate environment advances, the relevance of secretarial audits in maintaining the integrity and credibility of business operations grows, making them an essential tool for businesses of all sizes.
CS Urvashi Jain is an associate member of the Institute of Company Secretaries of India. Her expertise, inter-alia, is in regulatory approvals, licenses, registrations for any organization set up in India. She posse’s good exposure to compliance management system, legal due diligence, drafting and vetting of various legal agreements. She has good command in drafting manuals, blogs, guides, interpretations and providing opinions on the different core areas of companies act, intellectual properties and taxation.
Categories
- Agreement Drafting (23)
- Annual Compliance (13)
- Change in Business (37)
- Company Law (150)
- Compliance (90)
- Digital Banking (3)
- Drug License (4)
- FEMA (17)
- Finance Company (42)
- Foreign Taxation (9)
- FSSAI License/Registration (15)
- GST (123)
- Hallmark Registration (1)
- Income Tax (213)
- Latest News (34)
- Miscellaneous (170)
- NBFC Registration (8)
- NGO (18)
- SEBI Registration (6)
- Section 8 Company (10)
- Start and manage a business (27)
- Startup/ Registration (134)
- Trademark Registration/IPR (48)
Recent Posts
All Website Tags
About us
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost.








